Role of Cholestyramine in Refractory Hyperthyroidism: A Case Report and Literature Review
-
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune disease is when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues, often linked to imbalances in the microbiome, which can disrupt immune regulation and contribute to disease development.
-
Metals
Metals
OverviewHeavy metals play a significant and multifaceted role in the pathogenicity of microbial species. Their involvement can be viewed from two primary perspectives: the toxicity of heavy metals to microbes and the exploitation of heavy metals by microbial pathogens to establish infections and evade the host immune response. Understanding these aspects is critical for both […]
-
Microbes
Microbes
Microbes, short for microorganisms, are tiny living organisms that are ubiquitous in the environment, including on and inside the human body. They play a crucial role in human health and disease, functioning within complex ecosystems in various parts of the body, such as the skin, mouth, gut, and respiratory tract. The human microbiome, which is […]
Microbiome Signatures identifies and validates condition-specific microbiome shifts and interventions to accelerate clinical translation. Our multidisciplinary team supports clinicians, researchers, and innovators in turning microbiome science into actionable medicine.
Karen Pendergrass is a microbiome researcher specializing in microbiome-targeted interventions (MBTIs). She systematically analyzes scientific literature to identify microbial patterns, develop hypotheses, and validate interventions. As the founder of the Microbiome Signatures Database, she bridges microbiome research with clinical practice. In 2012, based on her own investigative research, she became the first documented case of FMT for Celiac Disease—four years before the first published case study.
What was studied?
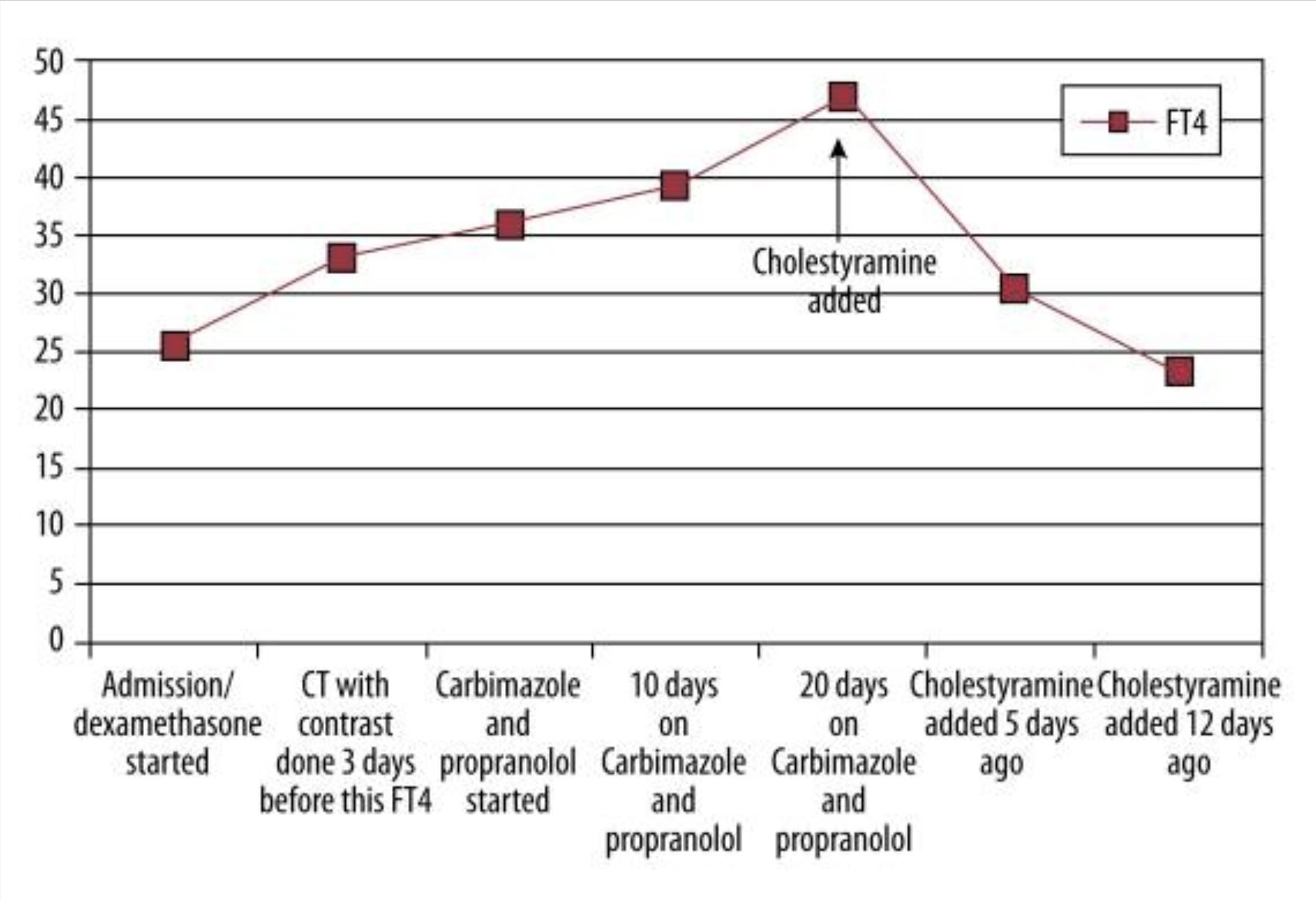
The study investigated the role of cholestyramine as an additional treatment for refractory iodine-induced hyperthyroidism in a patient who did not respond to conventional therapies.
Who was studied?
A 52-year-old female patient with a history of goiter who developed iodine-induced hyperthyroidism following a CT scan with contrast. The patient had obstructive symptoms and was unresponsive to standard treatments, including dexamethasone, carbimazole, and propranolol.
What were the most important findings?
After adding cholestyramine, the patient’s FT4 levels decreased by 30% within 5 days and normalized by 12 days.
What are the greatest implications of this study?
Cholestyramine can be an effective adjunct therapy for managing refractory iodine-induced hyperthyroidism, suggesting a potential new treatment avenue for similar cases, such as Grave’s Disease (GD). This case highlights the need for alternative treatments when conventional therapies fail and emphasizes the utility of cholestyramine in rapid thyroid hormone reduction.